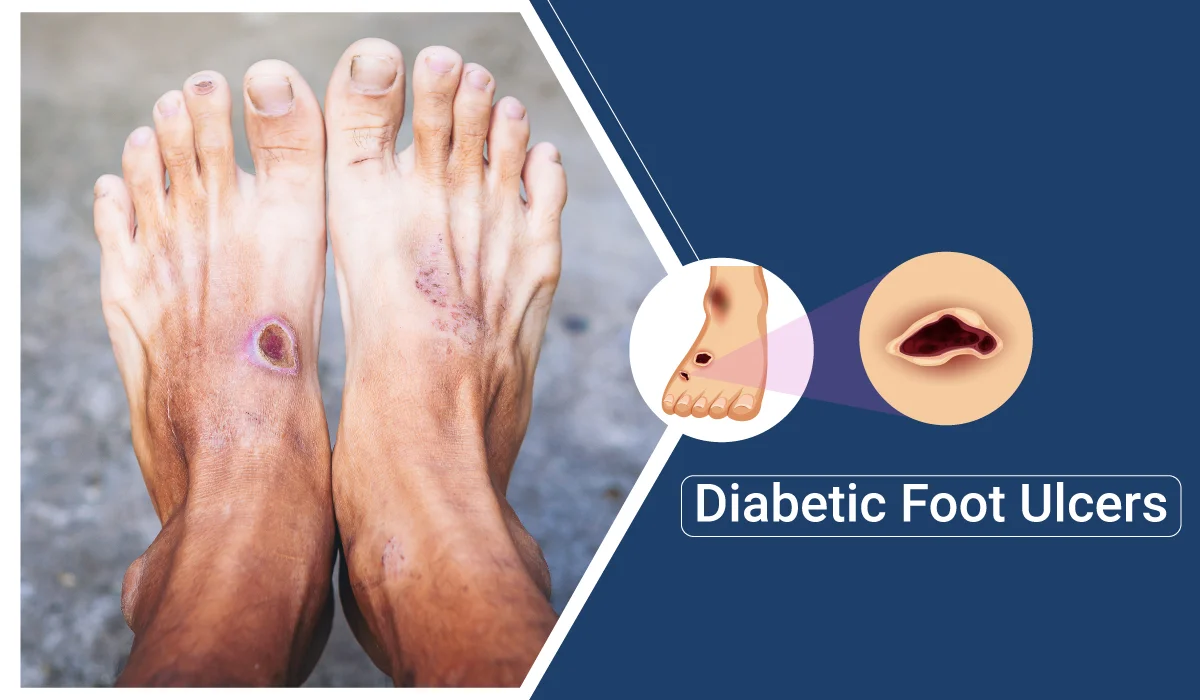
Living with diabetes involves careful management of various health risks, one of which is the development of diabetic foot ulcers. These ulcers, while common among individuals with diabetes, require attention and understanding for proper prevention, treatment, and care.
What are Diabetic Foot Ulcers?
Diabetic foot ulcers are open sores or wounds that occur on the feet of individuals with diabetes. They typically develop due to a combination of factors, including nerve damage (neuropathy), reduced blood circulation, and increased vulnerability to infection. Often, these ulcers form on pressure points like the sole of the foot or areas where footwear may rub against the skin.
Importance of Prevention
Preventing diabetic foot ulcers is crucial for individuals managing diabetes. Simple yet effective measures can significantly reduce the risk:
- Proper Foot Care: Regularly inspect feet for any cuts, blisters, or redness. Keep feet clean and moisturized, and trim toenails carefully to avoid ingrown nails.
- Wear Suitable Footwear: Opt for comfortable shoes that fit well, avoiding tight or ill-fitting footwear that may cause friction or pressure.
- Manage Blood Sugar Levels: Keeping blood sugar within a healthy range can aid in preventing nerve damage and promoting better circulation, reducing the risk of ulcers.
- Regular Check-ups: Visit a healthcare professional regularly, especially if there are concerns about foot health.
Treatment and Management
When diabetic foot ulcers do occur, prompt treatment is crucial to prevent complications such as infections or more severe tissue damage. Treatment may involve:
- Wound Care: Cleaning the wound regularly, using appropriate dressings, and keeping weight off the affected foot to promote healing.
- Infection Control: Antibiotics may be necessary if an infection develops. Close monitoring is crucial to prevent the spread of infection.
- Debridement: Removing dead or infected tissue from the wound to facilitate healing.
- Offloading Pressure: Using special footwear or devices to reduce pressure on the ulcer, allowing it to heal.
The Role of Comprehensive Care
Managing diabetic foot ulcers requires a holistic approach involving healthcare professionals, including podiatrists, vascular surgeons, plastic surgeons, General Surgeons, endocrinologists, and wound care specialists. They can provide guidance on wound care, offer advice on footwear, and monitor healing progress.
Embracing Lifestyle Changes
Beyond medical intervention, adopting a healthy lifestyle plays a pivotal role in managing diabetes and preventing complications such as foot ulcers. This includes:
- Balanced Diet: Eating a nutritious diet helps in managing blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity improves circulation and overall health.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking impairs circulation and hampers wound healing.
Conclusion
Diabetic foot ulcers demand attention and proactive measures to prevent, treat, and manage effectively. With diligent foot care, proper treatment, and a focus on overall health and lifestyle adjustments, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of these ulcers and ensure optimal foot health, enhancing their quality of life.
Remember, consulting healthcare professionals and psychologist who give patient counselling for personalized guidance is crucial in managing diabetic foot ulcers. With the right approach and care, it’s possible to navigate diabetes while minimizing the risks associated with foot ulcers.